Welcome to the Amira-Avizo Software Use Case Gallery
Below you will find a collection of use cases of our 3D data visualization and analysis software. These use cases include scientific publications, articles, papers, posters, presentations or even videos that show how Amira-Avizo Software is used to address various scientific and industrial research topics.
Use the Domain selector to filter by main application area, and use the Search box to enter keywords related to specific topics you are interested in.
3D characterisation of the particle kinematics during loess collapse is performed based on X-ray micro-computed tomography.
Particle displacements and rotations associated with the collapse are determined.
The volumetric strain is shown to be significantly heterogeneous at single-particle scale.
The evolution of particle-to-particle contacts is found to be much more complex than previously stated.
An apparatus is specially designed to perf... Read more
B. Yu, W. Fan, J.H. Fan, T.A. Dijkstra, Y.N. Wei, T.T. Wei
The prevailing electrode fabrication method for lithium-ion battery electrodes includes calendering at high pressures to densify the electrode and promote adhesion to the metal current collector.
However, this process increases the tortuosity of the pore network in the primary transport direction and imposes severe tradeoffs between electrode thickness and rate capability. With the aim of understanding the impact of pore tortuosity on electrode kinetics, and enabling cell designs with ... Read more
Benjamin Delattre, Ruhul Amin, Jonathan Sander, Joël De Coninck, Antoni P. Tomsia and Yet-Ming Chiang
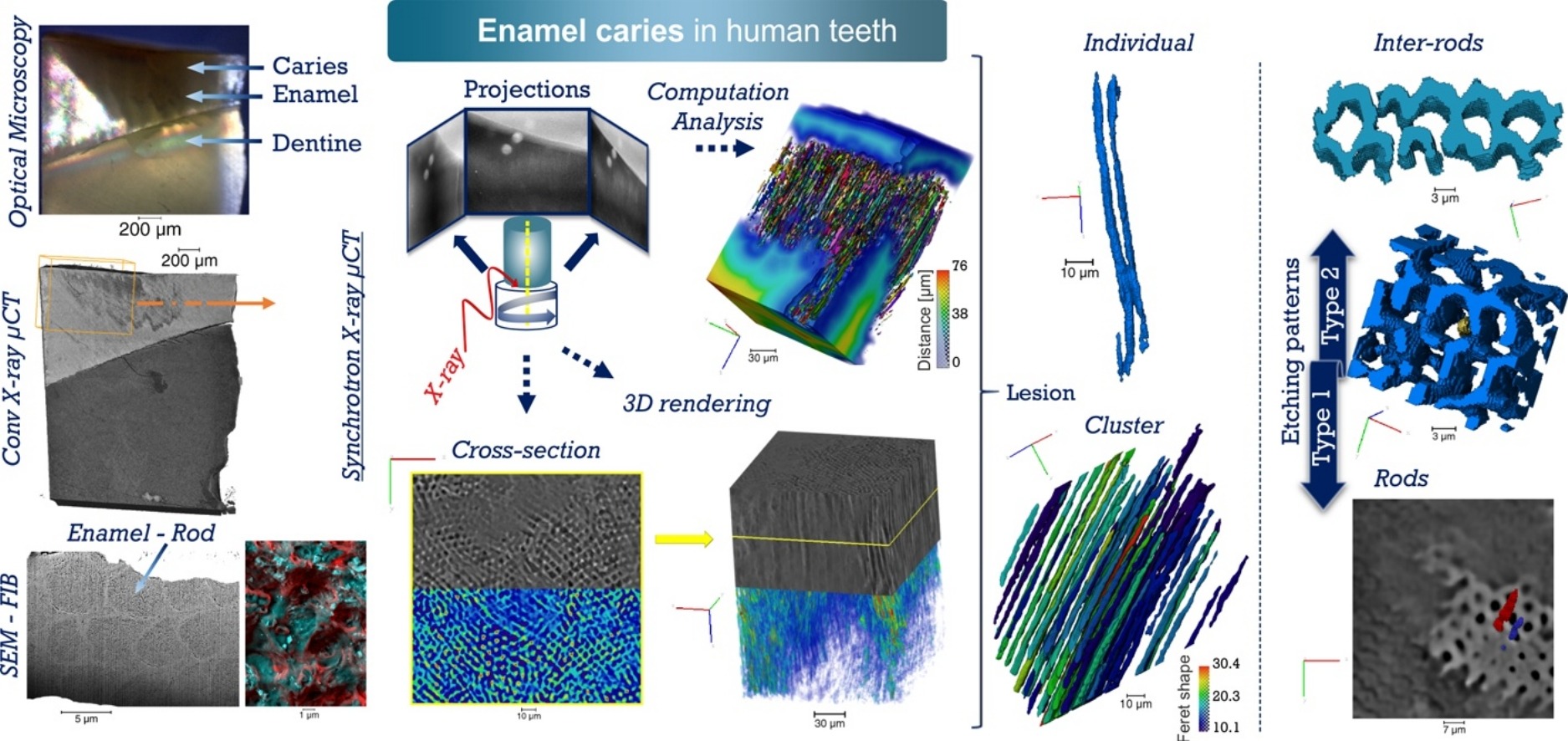
Unprecedented combination of resolution, field of view and contrast for the analysis human enamel carious lesions was achieved. Synchrotron X-ray micro-computed tomography revealed sub-micron details of enamel rod and inter-rod regions inaccessible by laboratory tomography. Successful segmentation and labelling allowed the extraction of enamel etching patterns and statistics. Correlation was obtained between synchrotron X-ray micro-tomography and FIB-SEM cross-sec... Read more
Cyril Besnard, Robert A. Harper, Thomas E. J. Moxham, Jonathan D. James, Malte Storm, Enrico Salvati, Gabriel Landini, Richard M. Shelton, Alexander M.Korsunsky
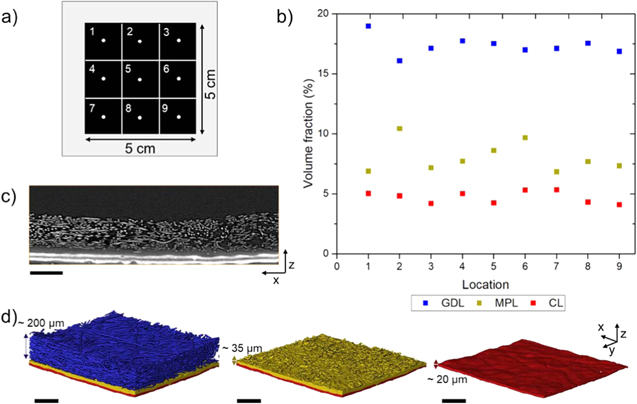
With the growing use of X-ray computed tomography (X-ray CT) datasets for modelling of transport properties, comes the need to define the representative elementary volume (REV) if considering three dimensions or the representative elementary area (REA) if considering two dimensions. The resolution used for imaging must be suited to the features of interest in the sample and the region-of-interest must be sufficiently large to capture key information. Polymer electrolyte fuel cells have a hier... Read more
Jennifer Hack et al 2020 J. Electrochem.
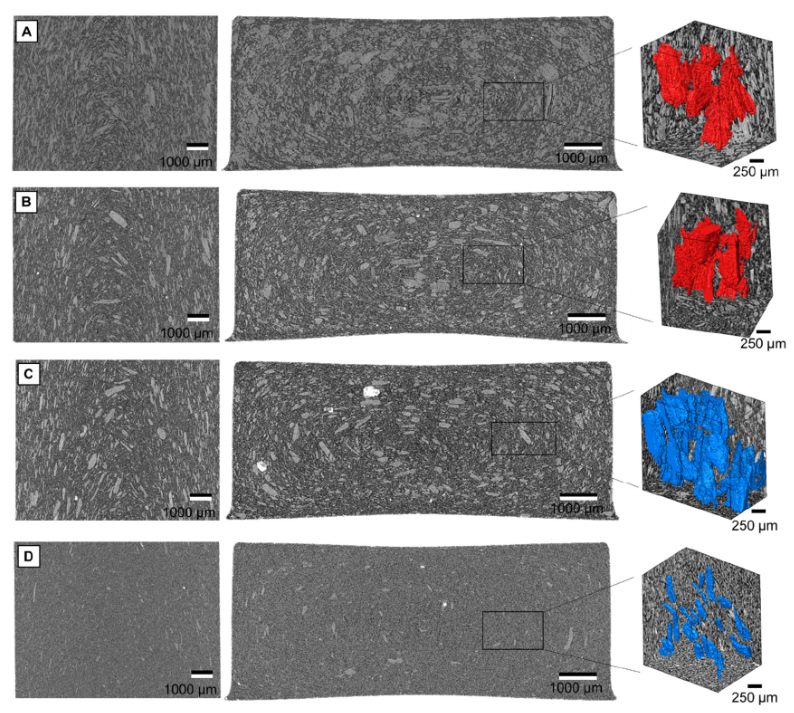
In this study, various wood material sources were used for the manufacture of wood-polymer composites (WPC). The materials were categorised as virgin wood particles (VWP), reprocessed WPC particles (RWP) and recycled thermoset composite particles (RCP) and derived from two virgin wood sources, three-layer particle boards, medium-density fibre boards (MDF) boards,or two different wood/polypropylene composites. All produced wood-polypropylene compounds contained 60% wood material and were manu... Read more
Kim Christian Krause, D, Philipp Sauerbier, Tim Koddenberg and Andreas Krause
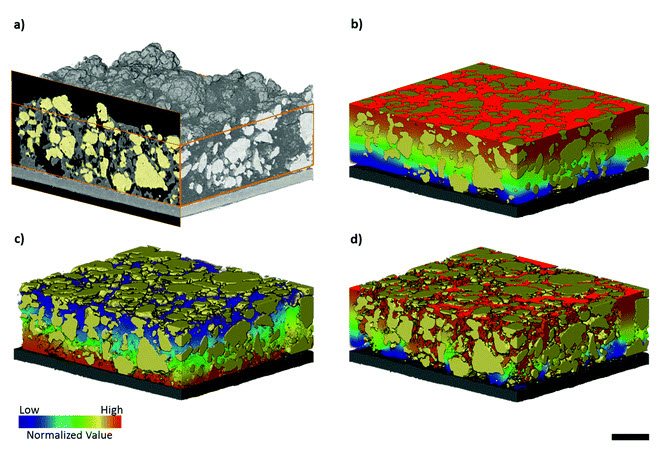
Three-dimensional image based modelling of transport parameters in lithium–sulfur batteries
An elemental sulfur electrode was imaged with X-ray micro and nano computed tomography and segmented into its constituent phases. Morphological parameters including phase fractions and pore and particle size distributions were calculated directly from labelled image data, and flux based simulations were performed to determine the effective molecular diffusivity of the pore phase and electrical conductivity of the conductive carbon and binder phase, D... Read more
Chun Tan, Matthew D. R. Kok , Sohrab R. Daemi , Daniel J. L. Brett and Paul R. Shearing
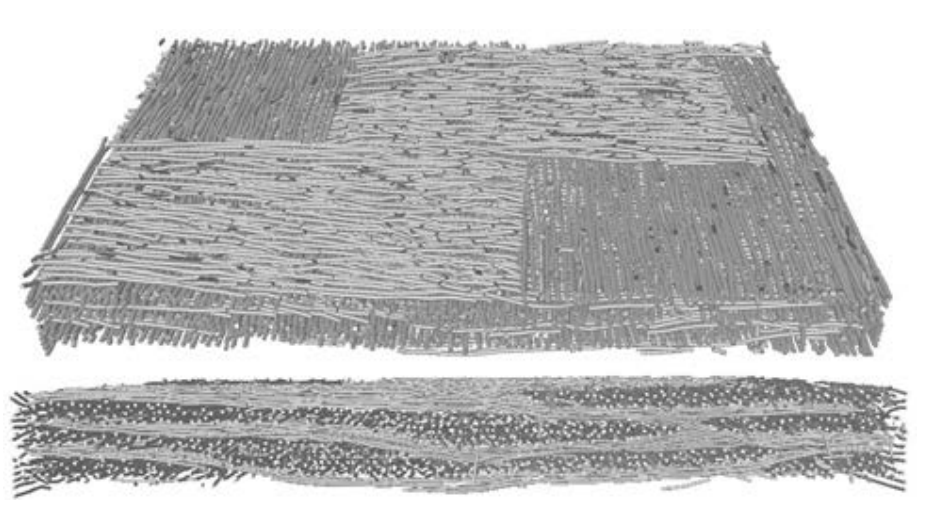
The paper proposes a new experimental methodology, based on ultrasonic measurements, that aims at evaluating the anisotropic damage in woven semi-crystalline polymer composites through new damage indicators. Due to their microstructure, woven composite materials are characterized by an anisotropic evolution of damage induced by different damage mechanisms occurring at the micro or mesoscopic scales. In this work, these damage modes in polyamide 6.6/6-woven glass fiber reinforced composites ha... Read more
Pascal Pomarède, Fodil Meraghni, Laurent Peltier, Stéphane Delalande, Nico F. Declercq
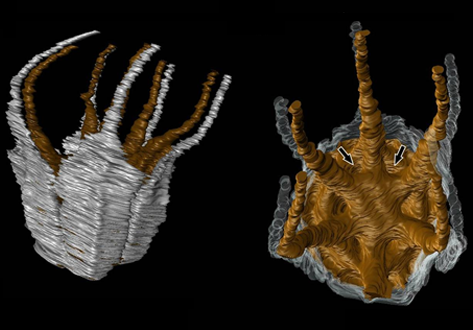
Angiosperm-dominated floras of the Late Cretaceous are essential for understanding the evolutionary, ecological, and geographic radiation of flowering plants.
The Late Cretaceous–early Paleogene Deccan Intertrappean Beds of India contain angiosperm-dominated plant fossil assemblages known from multiple localities in central India. Numerous monocots have been documented from these assemblages, providing a window into an important but poorly understood time in their diversification. On... Read more
Kelly K.S. Matsunaga, Selena Y. Smith, Steven R. Manchester, Dashrath Kapgate, Deepak Ramteke, Amin Garbout, and Herminso Villarraga-Gómez
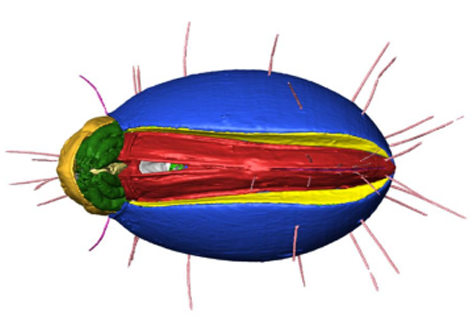
The NOVA project: maximizing beam time efficiency through synergistic analyses of SRµCT data
Beamtime and resulting SRμCT data are a valuable resource for researchers of a broad scientific community in life sciences. Most research groups, however, are only interested in a specific organ and use only a fraction of their data. The rest of the data usually remains untapped. By using a new collaborative approach, the NOVA project (Network for Online Visualization and synergistic Analysis of tomographic data) aims to demonstrate, that more efficient use of the valuable beam time is possi... Read more
The international society for optics and photonics (SPIE)